On September 8th, Google stirred the search engine pot by giving an official kick-off to Google Instant.
In a nutshell, Google Instant tries to help users find information by showing relevant information as a query is typed. You have to keep in mind that this isn’t entirely new. Google (and many other search engines and browsers) have had autocomplete functionality for a long time.
Per Google: How it works
As a user starts to type a search, Google Instant automatically shows results for a popular search that begins with those letters. An algorithm tries to predict what the rest of the query might be based on popular queries typed by other users. The predicted text is shown in light grey in the search box, and search results and ads are automatically shown for that predicted query.
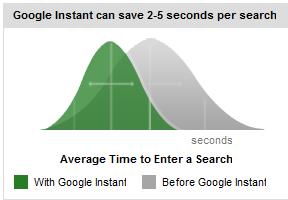
Google says that Google Instant is aimed at providing time savings to the end user. The core belief is that we search too slow and that our ability to find relevant information can be accelerated. Google Instant claims that the typical searcher took 9 seconds to enter a search phrase and that Google Instant can save 2-5 seconds per search.
The problem for brands goes far beyond “time savings”
When you examine the results for Google Instant, the new results are a new layer of real-time and popular consensus brand data about your brand name. This could be a company name, product or personal executive name.
Creating a virtual fork in the road
A large challenge for businesses and Google Instant revolve around any brand that has a generic keyword or location keyword. An example of this could be a local example such as the Seattle PI. When you search for the term “Seattle PI” – Google Instant gives you these results

Without any real understanding, readers familiar with the Seattle PI may be having a Google induced urge to get some Seattle Pizza.
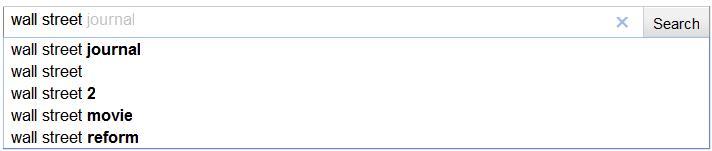
On a larger brand scale, users looking for the Wall Street Journal are encouraged to look at secondary items as soon as “wall street” is typed in.
Why is this important?
This process fundamentally changes the way we find information online. Searching for information used to be an individual and personal process. It also supported the idea that you had a semi-complete train of thought when searching.
Google Instant assumes you don’t have a complete concept and tries to predict incomplete and partial thoughts to the popular consensus items it knows about. This means that real research and due-diligence is contaminated by another layer of invisible social and search data.
Ultimately Google Instant means that you are in competition for your brand keywords for EVERY LETTER in the search process.
Advertising Brand Overload
If we look at a popular brand such as NIKE and how it interacts with Google Instant, not only are the organic results affected… but as every letter of the search is completed we are presented with dozens (if not hundreds) of ad impressions from Google Adwords.
The following graphic details how the search box and ads change as I type “NIKE” into Google. You can see how quickly brand degradation occurs as Google Instant pushes us through brand exposure of Netflix, Nordstrom, NPR, Nissan, Ninetendo and Nikon before we get to “NIKE”
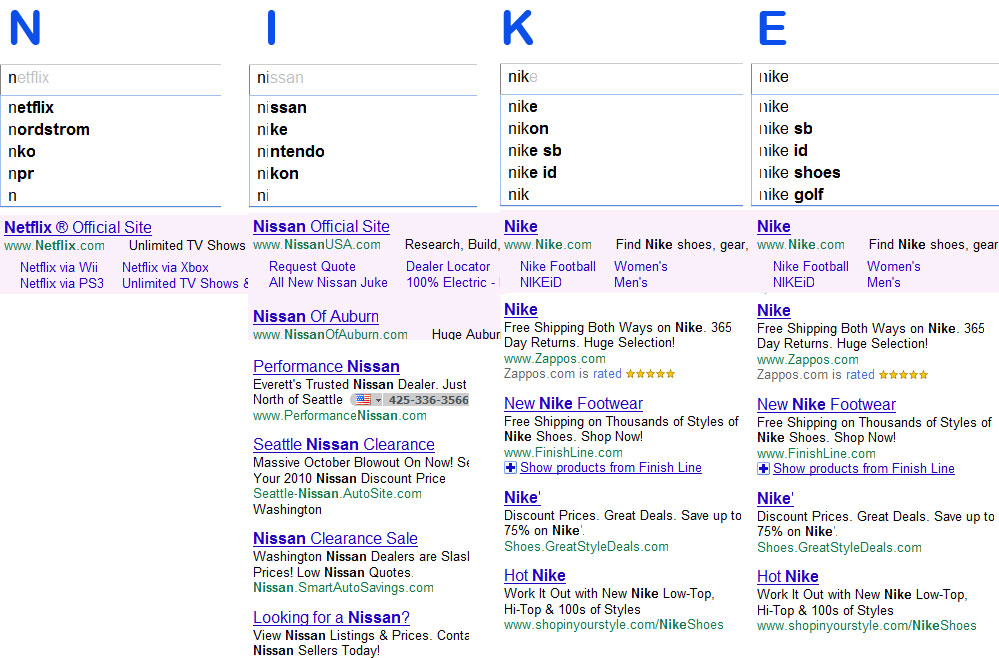
Even with something as simple and short as the keyword “NIKE”, we can quickly see how Google is contaminating our brand equity. The longer the search phrase required to find your business, the more impressions Google is serving to our current brand audience.
If your business has an active search engine optimization or search marketing component, you should spend some quality time understanding the core components of your business model that are being shifted around and monetized by Google.